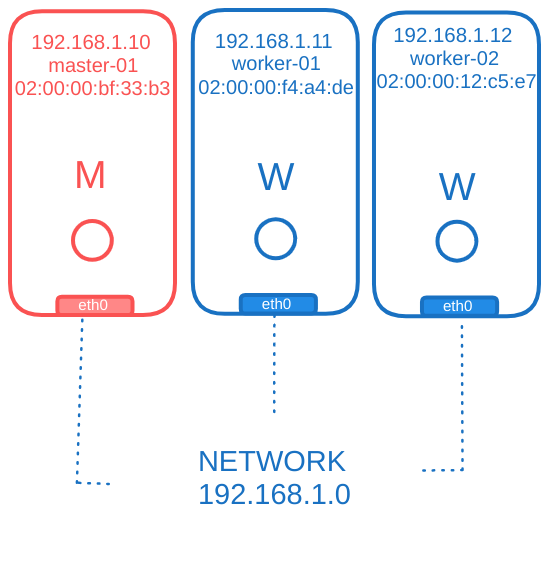
The Kubernetes cluster consists of master and worker nodes, each requiring specific network setups.
Network Requirements for Nodes
-
Network Interfaces:
- Each node must have at least one interface connected to a network.
- Each interface must have a configured address.
-
Host Configuration:
- Each host must have a unique hostname and a unique MAC address.
- Ensure uniqueness, especially if VMs were cloned from existing ones.
Port Configurations
Various ports must be opened for different components in the control plane:
- API Server: Port
6443- Accessed by worker nodes, kube control tool, external users, and all other control plane components.
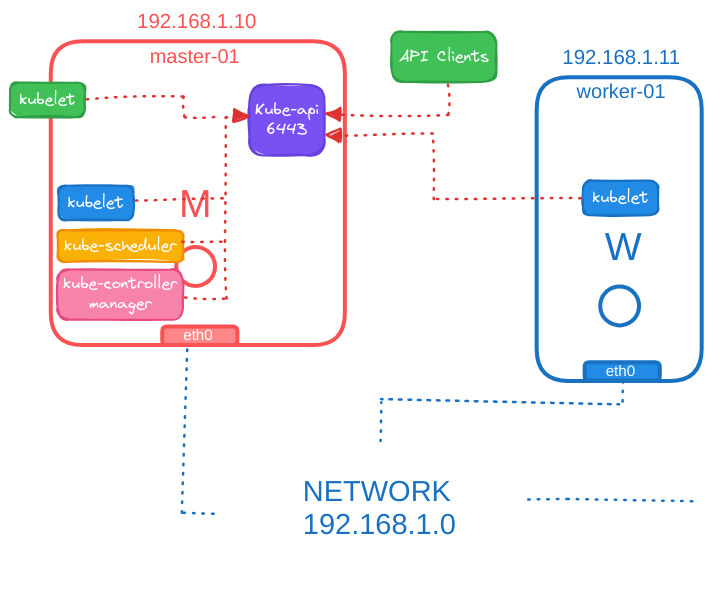
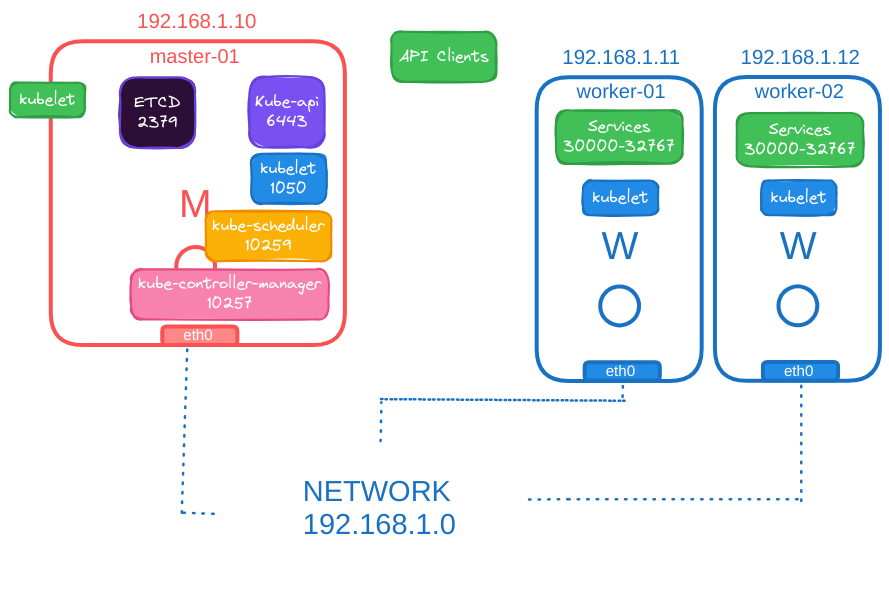
- Kubelet: Port
10250- Kubelets can be present on both master and worker nodes.
- Kube Scheduler: Port
10259 - Kube Controller Manager: Port
10257 - Service Exposure: Ports
30000-32767 - ETCD Server: Port
2379
Multiple Master Nodes:
- Open the same ports as a single master node.
- Additional Port
2380for ETCD clients to communicate.
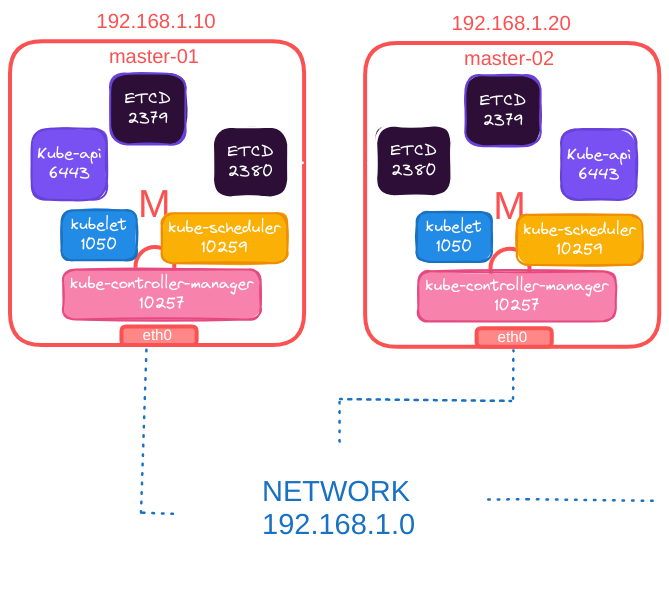
These port configurations are crucial and listed in the Kubernetes documentation. https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/networking/ports-and-protocols/
Therefore, when setting up networking for your nodes, consider the following:
- Configuring firewalls, IP table rules, or network security groups in cloud environments like GCP, Azure, or AWS.
- Ensuring these configurations to troubleshoot networking issues.